differences between male and female skeletons

There are three main differences between the male (A, in the illustration) and female (B) human skeletons. The male skeleton usually has:
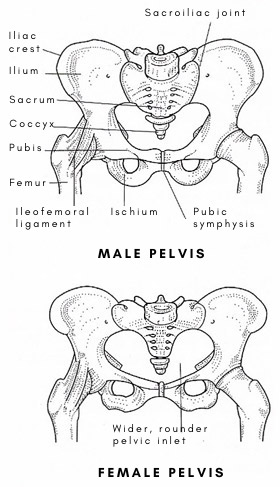 |
| The female pelvis is shallower and wider than that of the male. |
In general, male skeletons are larger and heavier than female skeletons. This is due to higher levels of testosterone in males, which stimulates bone growth and increases muscle mass. As a result, male skeletons tend to have larger bones, particularly in the arms, legs, and torso.
There are also general differences in the shape of male and female skeletons. Female skeletons tend to be more slender and delicate, with smaller bones and more curves. Male skeletons, on the other hand, tend to be more rectangular and sturdy, with broader shoulders and a more linear frame. These differences in shape are due to differences in muscle mass and distribution, as well as hormonal influences on bone growth and development.
In addition to differences in size and shape, there are also differences in the distribution of bone density and muscle mass between male and female skeletons. Female skeletons tend to have a higher proportion of bone mass in the pelvis, spine, and lower limbs, while male skeletons tend to have more bone mass in the upper limbs, ribs, and skull. This difference in bone density is due to the different roles that males and females played in human evolution, with males typically performing more physically demanding tasks that required stronger upper body strength.


