dynamic pressure
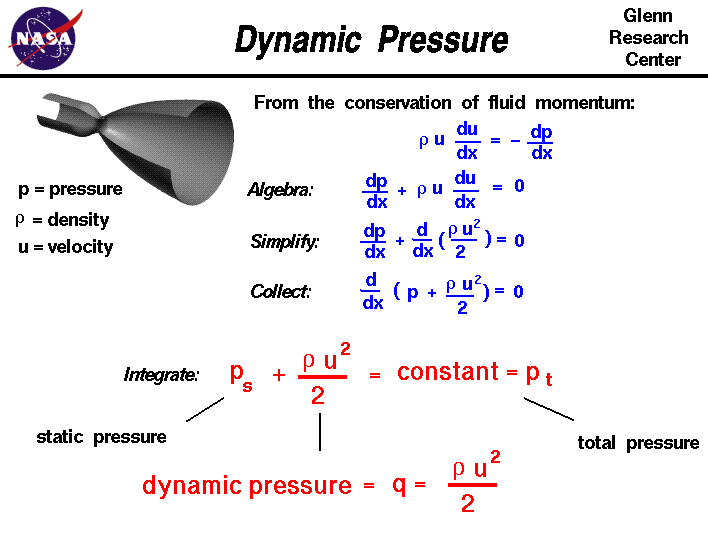
Dynamic pressure is the pressure of a fluid, such as air, that results from its motion, or the pressure exerted on a body, because of its motion through a fluid. Dynamic pressure is equal to one-half the fluid density, ρ, multiplied by the square of the fluid's velocity, u. That is, dynamic pressure = ½ρu 2. In incompressible flow, the dynamic pressure is the difference between the total pressure and the static pressure. It is designated by the letter "q."


