penis
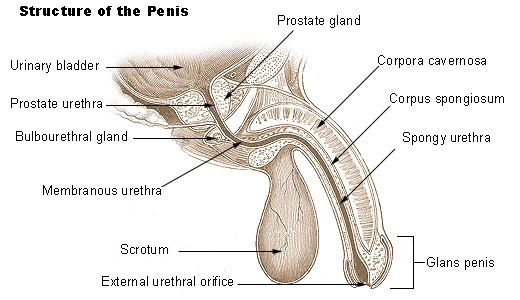
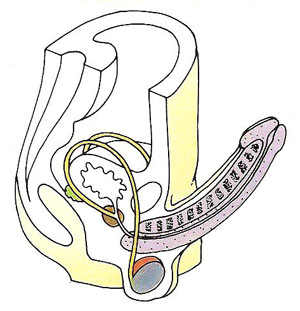
The penis is the male copulatory organ and part of the male reproductive system. It is a cylindrical pendant organ located anterior to the scrotum and functions to transfer sperm to the vagina. The penis consists of three columns of erectile tissue that are wrapped in connective tissue and covered with skin. The two dorsal columns are the corpora cavernosa. The single, midline ventral column surrounds the urethra and is called the corpus spongiosum.
The penis has a root, body (shaft), and glans penis. The root of the penis attaches it to the pubic arch and the body is the visible, pendant portion. The corpus spongiosum expands at the distal end to form the glans penis. The urethra, which extends throughout the length of the corpus spongiosum, opens through the external urethral orifice at the tip of the glans penis. A loose fold of skin, called the prepuce, or foreskin, covers the glans penis.
Just before orgasm, the penis, which is at its maximum length, exudes drops of semen (seminal fluid). These may contain viable sperm which is why withdrawal is ineffective as a contraceptive method. On orgasm, muscular contractions occur at the base of the penis and bring about ejaculation.


