magnetic declination
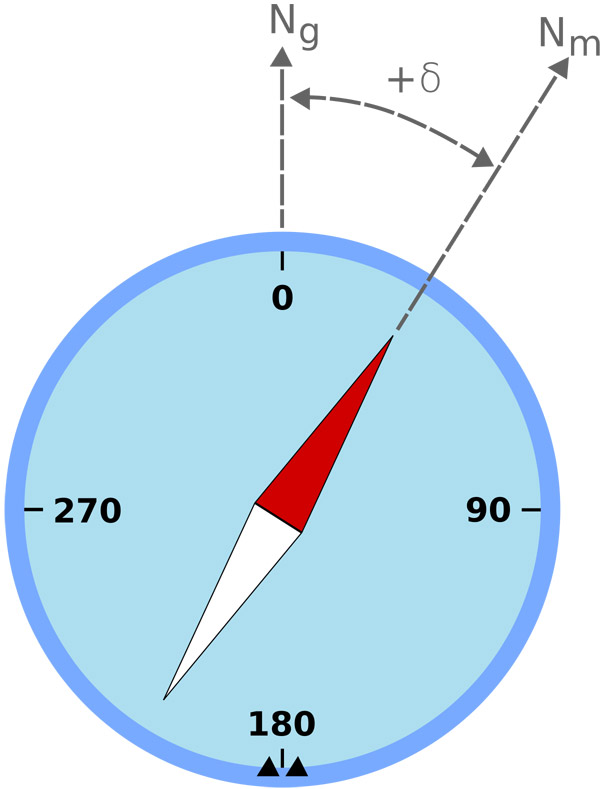
Example of magnetic declination showing a compass needle with a "positive" (or "easterly") variation from geographic north. Ng is geographic or true north, Nm is magnetic north, and δ is magnetic declination.
Magnetic declination, also called magnetic deviation (δ), is the amount by which the direction indicated by a magnetic compass differs from the direction of true north. It arises because the magnetic north pole is not coincident with the true North Pole. As a result, declination varies from place to place on Earth's surface. Also, because the north magnetic pole slowly moves over time, declination varies from year to year. Angles to the east of true north are taken as positive; angles to the west are negative.
Magnetic inclination
Magnetic inclination, also called magnetic dip, is the direction between Earth's magnetic field and the horizontal, measured by a free-floating magnet. At the north magnetic pole the inclination is zero; at the magnetic equator it is 90°.


