mononucleosis
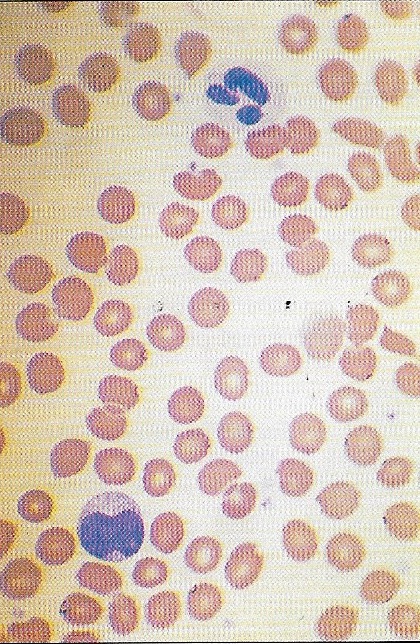
Mononucleosis may be diagnosed by a blood test that reveals large, atypical mononuclear cells (blue cell, at bottom), as seen in this micrograph. .
Mononucleosis, also called glandular fever, is a common virus infection of adolescence causing a variety of symptoms including severe sore throat, headache, fever, malaise, and enlargement of lymph nodes and spleen. Skin rashes, hepatitis with jaundice, pericarditis, and involvement of the nervous system may also be prominent. Atypical lymphocytes in the blood and specific agglutination reactions are diagnostic. Severe cases may require steroids and convalescence may be lengthy. It can be transmitted in saliva and has thus been nicknamed the "kissing disease." The infection is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus.


