Gram's stain
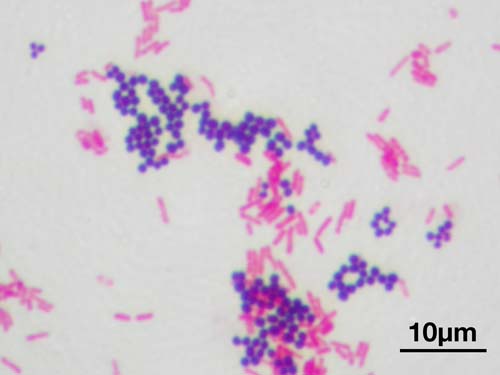
A Gram stain of mixed Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus ATCC 25923, Gram-positive cocci, in purple) and Escherichia coli (E. coli ATCC 11775, Gram-negative bacilli, in red), the most common Gram stain reference bacteria
In microbiology, Gram's stain is a differential staining method named after the Danish physician Hans Christian Gram (1853–1938). It aids in the categorizing and identification of bacteria, which are said to be Gram-positive or Gram-negative, depending on whether or not they retain the original violet stain at the end of the process. If Gram-negative, the stain washes out to a red counterstain.


