gene mapping
Gene mapping – also called linkage mapping – can offer firm evidence that a disease transmitted from parent to child is linked to one or more genes. Mapping also provides clues about which chromosome contains the gene and precisely where the gene lies on that chromosome.
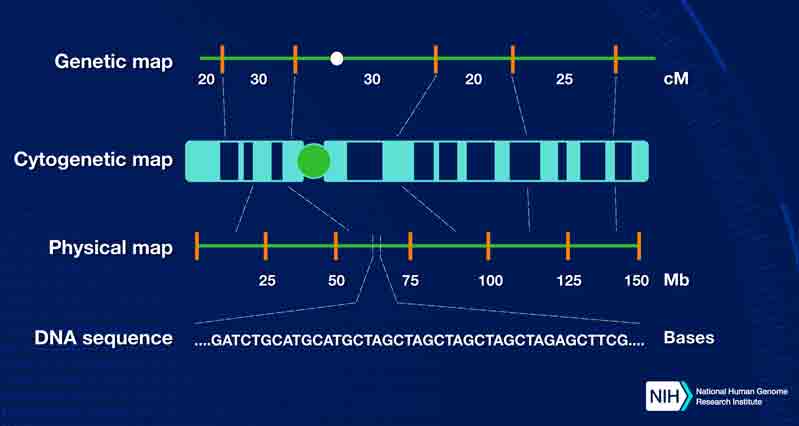
Gene mapping is determining the relative positions of genes on a chromosome and the distance between them. Gene mapping is crucial to understanding and developing treatments for genetic disease.
There are two different methods of gene mapping:
· genetic mapping
· physical mapping
Gene mapping uses "linkage analysis" to determine the relative position of genes within a chromosome. If both genes are inherited together they are considered linked. By determining which genes are linked, the relative positions of genes can be worked out.
Physical mapping involves finding the exact position of a specific gene within a chromosome. Various techniques have been developed to do this, including creating cell hybrids for mapping out DNA in specific chromosomes.


