adaptations of fish
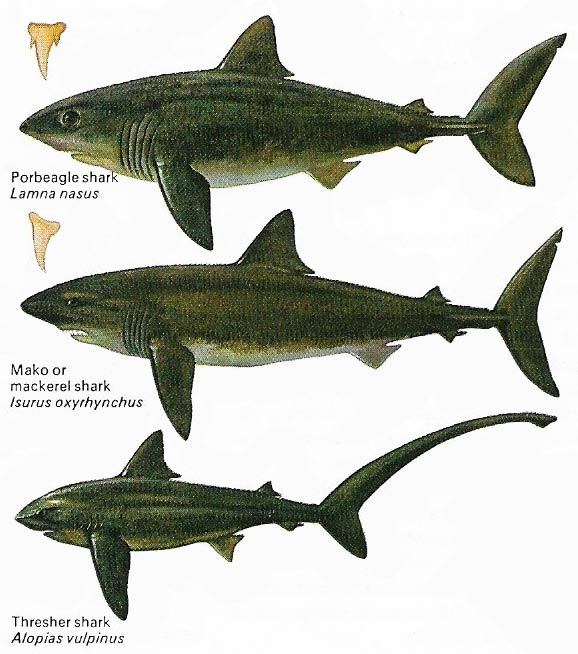
Figure 1. All these shark species are known to venture into European waters. Like other typical sharks (Elasmobranchii) they are predatory fish renowned for their swimming speed and ferocity.
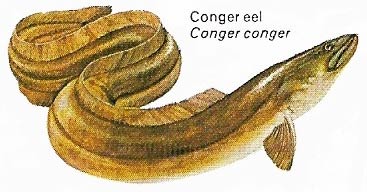
Figure 2. The conger eel, the largest of all eels (order Anguilliformes) is found in the Mediterranean and Atlantic as far north as Scandinavia. It commonly reaches 2 m (6.5 ft) and weighs 30–35 kilograms (66–77 pounds).
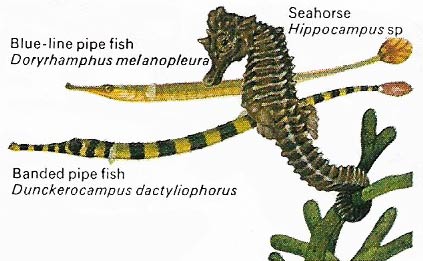
Figure 3. One of the ocean's oddities, the seahorse, is related to the pipefish and to the stickleback. These fish have bodies covered, in varying degree, with bony plates and have tubular snouts.
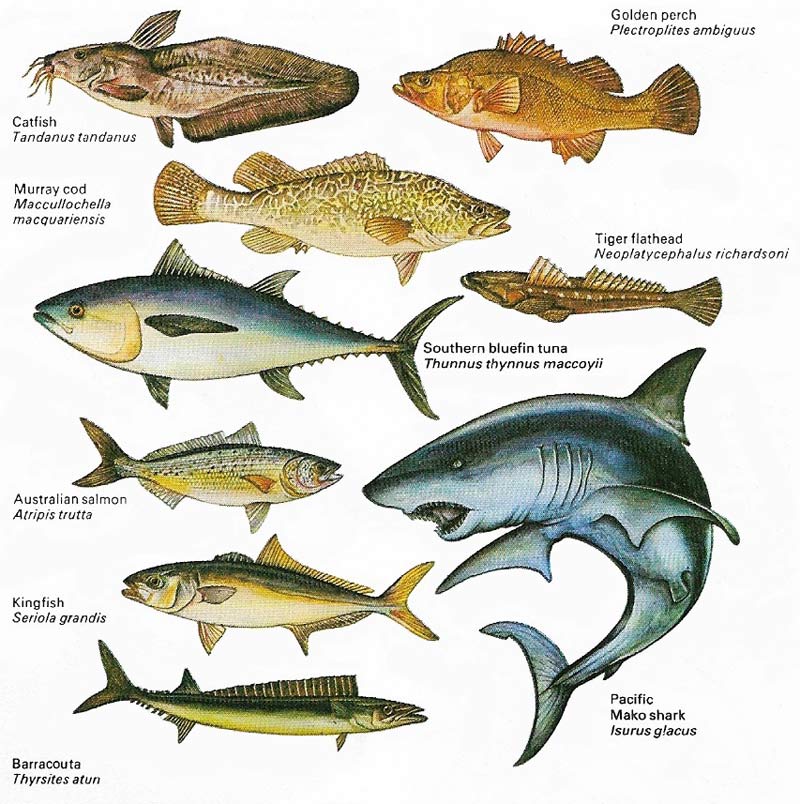
Figure 4. Australian waters are inhabited by about 2,000 species of fish. Sharks and barracudas patrol the seas and inland waters abound in freshwater types, including the catfish and the murray cod.

Figure 5. One of man's most important food fish is the herring. It is classified in the order Clupeiformes and is found on both sides of the North Atlantic. Its average length is 30 centimeters (12 inches).
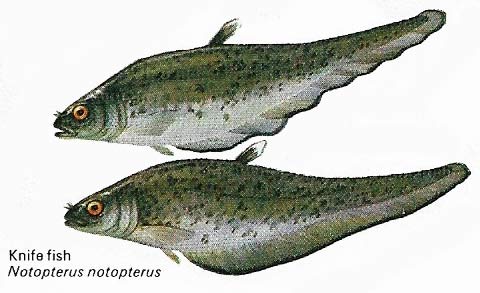
Figure 6. Weedy regions of rivers and backwaters in Southern Asia are the home of the knife fish. The fish are named after their vertically compressed shape. Their color varies widely, even within one species, which makes them hard to identify.
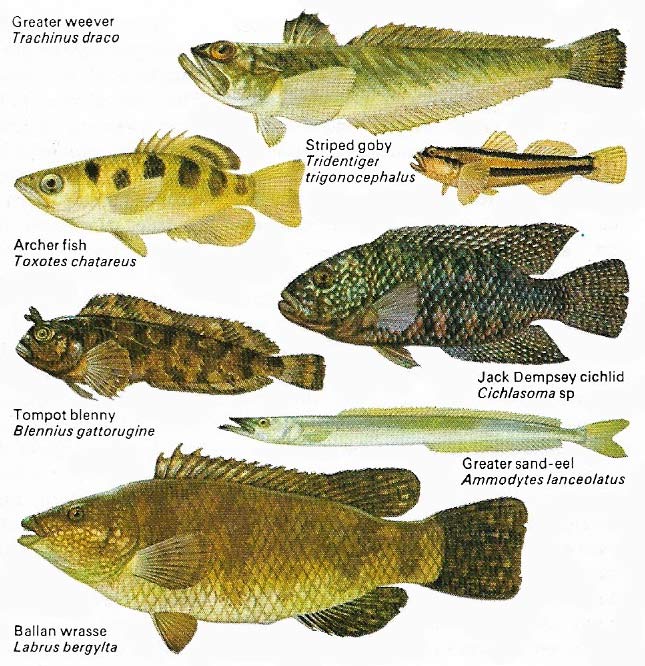

Figure 7. A great variety of species are placed in the order Perciformes – the perch-like fish. They live in both fresh and salt water. The greater weever, tompot blenny, greater sand-eel and ballan wrasse inhabit the Mediterranean and northeast Atlantic. The River Amazon is the home of the Jack Dempsey cichlid, while both the archer fish of estuaries and the striped goby of coasts come from South-East Asia.
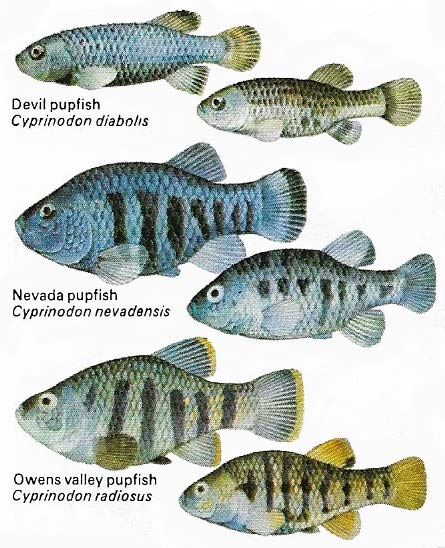

Figure 8. These three species of pupfish live in the vestiges of Lake Lahontan in Nevada. These desert fish are the remains of a huge aquatic fauna. Equally rare is the Lahontan cutthroat trout.

Figure 9. The waters of Japan are renowned for their wide variety of fish – a mixture of tropical, Indo-Pacific species and others from northern waters. The puffer fish is a Japanese delicacy.
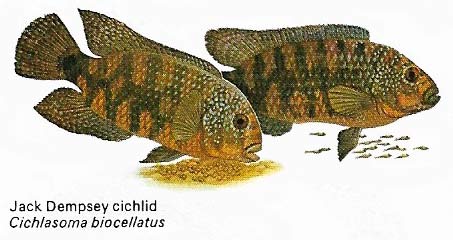
Figure 10. The cichlids, perch-like fish of Africa and of South and Central America, show interesting parental care. Both sexes may take turns to fan and guard nests, eggs and fry, from potential predators.
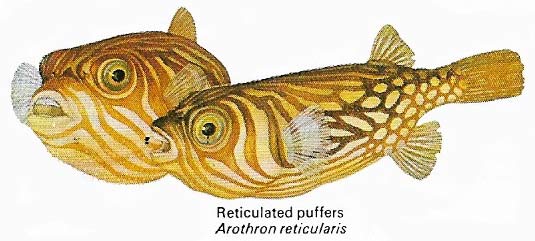
Figure 11. The ability to blow themselves up when danger threatens has given the puffer fish their name. Puffers tend to be aggressive but fights between individuals seldom prompt full distension.
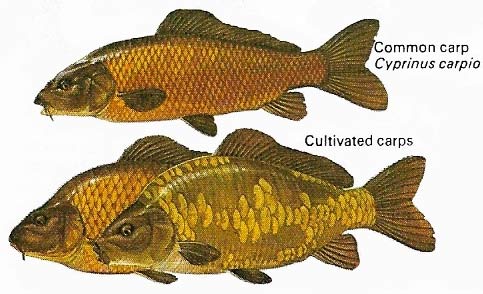
Figure 12. The carps are bony fish belonging to the order Cypriniformes. Their large bodies are usually covered evenly with large scales but these may be missing in cultivated types such as the mirror carp.
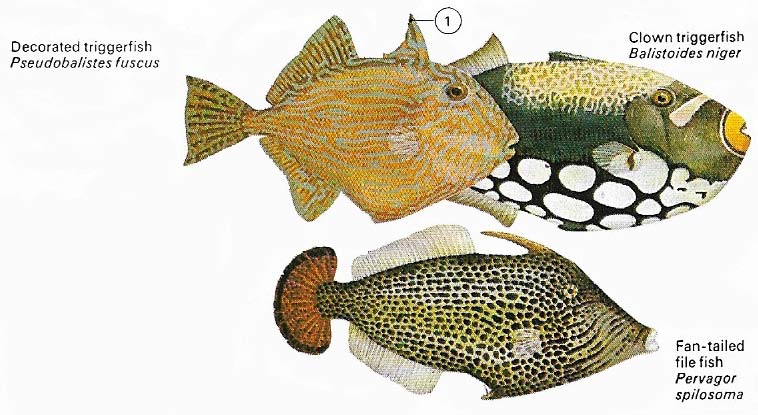
Figure 13. The triggerfish and file fish are co-inhabitants of warm Pacific waters. When alarmed they retreat into coral cavities and erect their fin spines (1) to make themselves immovable.
Fish are found in an extraordinarily wide range of shapes and sizes. This reflects the many different ways in which they have become adapted to the various conditions and habitats that the world's seas and fresh waters have to offer. Many fish that live in weedy habitats, for example, have peculiar outgrowths from their bodies while others are decorated with intricate color patterns. Both these kinds of adaptations are forms of camouflage, as is the ability of some fish to change color to merge with their surroundings.
 |
| The sail fin leaf fish is a kind of scorpion fish. This coral reef fish can change color to blend with its surroundings and when alarmed may "act dead" by drifting upside down. |
A feature of fish that live in muddy waters are the sensory barbels round the mouth, which are used in locating food.
 |
| The name "catfish" is applied to a very large family of freshwater fish of the order Siluriformes which are sluggish in their movements and have barbels growing at their mouths. |
Predatory fish (Figure 1) are generally sleek and streamlined with large mouths and sharp teeth. Flatfish, in contrast, feed on the seabed and are slow-moving.
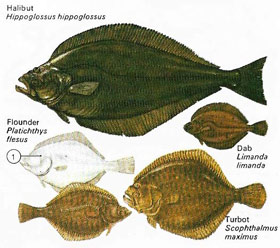 |
| The flatfish are classified in the order Pleuronectiformes. They really have "twisted" bodies, for as these fish develop the bones of the skull twist so that both eyes are on one side of the head. This side becomes the back of the mature flatfish and takes on a heavy pigmentation while the other, the "blind" side, remains nearly white. (1). Some species can change color as they move from Rocky to Sandy ocean bottom and vice versa. |
Fish of many kinds are vital to man as a source of food, particularly the cod (below), herring (Figure 5) and flatfish. Fish are also the source of fishmeal which is used in fertiliser and as pig and poultry feed. The fish, in turn, often feed upon other fish, their eggs and young.
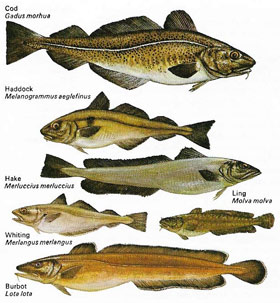 |
| The cod's and their allies are, to man, the most economically significant of all fish. Congregating in vast shoals, they may reach weights of over 80 kg (198 lb). The bourbon is a freshwater species. All belong to the order Gadiformes. |


