prednisone
Prednisone molecule.
Prednisone is a corticosteroid and immunosuppressant drug used to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms in a variety of disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and severe asthma.
Other disorders that are occasionally treated with prednisone include Addison's disease and blood disorders, such as leukemia. Prednisone is also used to prevent organ rejection after transplant surgery.
Large doses taken over a prolonged period may cause adverse effects typical of other corticosteroid drugs.
Pharmacology of prednisone
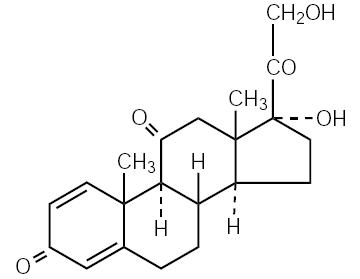
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid. Glucocorticoids are adrenocortical steroids, both naturally occurring and synthetic, which are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The chemical name for prednisone is pregna-1, 4-diene-3,11,20-trione, 17,21-dihydroxy-. The structural formula is shown in the diagram.
Prednisone is a white to practically white, odorless, crystalline powder. It is very slightly soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol, chloroform, dioxane, and methanol.
Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 5 mg, 10 mg or 20 mg of prednisone USP (anhydrous). In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, docusate sodium, magnesium stearate and sodium benzoate.


