pseudopodium
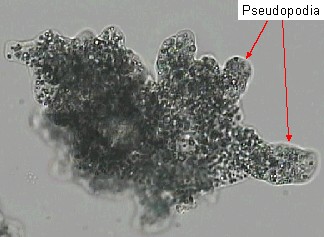
Amoeba.
A pseudopodium is a temporary extension ("false feet") of the cell membrane used for external movement (known as motility) or to engulf particles (known as phagocytosis). Pseudopodia are features of some protozoa, such as the amoeba, and of amoeboid cells, such as white blood cells.
They may be supported internally (actinopods) or not (rhizopoda), be threadlike (filose) or broad (lobose), may or may not bear extrusomes (nudipodia, extrusopodia), and may be produced one (monopodial) or many (polypodial) at one time.


