Holter monitor
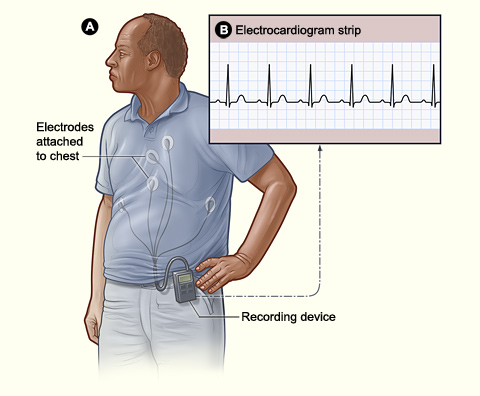
Figure A shows how a Holter or event monitor attaches to a patient. In this example, the monitor is clipped to the patient's belt and electrodes are attached to his chest. Figure B shows an electrocardiogram strip, which maps the data from the Holter or event monitor.
A Holter monitor is a device that continuously records the heart's rhythms while being worn, usually for 24 hours, during normal activity. A Holter monitor, also called an ambulatory electrocardiograph, is battery operated and carried in a pocket or a small pouch worn around the neck or waist. It is connected to electrodes (small conducting patches) that are stuck onto the patient's chest.
A Holter monitor records the heart's electrical activity. The patient keeps a diary of what activities he or she does while wearing the monitor. After 24 hours, the monitor is returned to the physician who matches the monitor's findings with the patient's symptoms and activities to determine if there have been any irregular heart rhythms. An event monitor is similar to a Holter monitor; however, an event monitor only records heart activity when symptoms occur.
Wireless Holter monitors
Wireless Holter monitors have a longer recording time than standard Holter monitors and record the heart's electrical activity for a preset amount of time. They are called wireless because they use a cell phone to send the data to the doctor's office. This happens automatically at certain times. These monitors still have wires that connect the device to the sensors stuck to the patient's chest.
A wireless Holter monitor can be used for days or even weeks until signs or symptoms of a heart rhythm problem occur. It is used especially to detect heart rhythm problems that don't occur often.
Although wireless Holter monitors work for longer periods, they have a down side. The patient must remember to write down the time of symptoms, so that his or her doctor can match it to the heart rhythm recording. Also, the batteries in the wireless monitor must be changed every 1 to 2 days.
Why the test is performed
Holter monitoring is used to determine how the heart responds to normal activity. The monitor may also be used:
It may be used to diagnose:
What abnormal results mean
Abnormal results may include various arrhythmias. Changes in the normal pattern of waves formed by the heart's electrical signals may mean that the heart is not getting enough oxygen.
Special considerations
Electrodes must be firmly attached to the chest so the machine gets an accurate recording of the heart's activity.
The patient should avoid magnets, metal detectors, electric blankets, and high-voltage areas while wearing the device.


