astrocyte
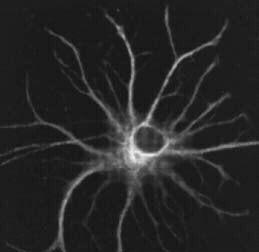
Rat brain astrocyte in culture, stained by immunofluorescence. Image credit: Robert Milner, Penn. State U.
An astrocyte is a star-shaped glial cell found in the central nervous system (CNS) (i.e., the brain and spinal cord). Astrocytes have many long arms or processes and are the largest and most numerous glial cells in the CNS; they outnumber neurons 10 to 1.
Astrocytes used to be thought of as mere gap fillers, with neurons responsible for all neurologically significant functions. But medical science now recognizes that astrocytes play a number of important active roles in the CNS. These include:
An astrocytoma is a tumor that begins in astrocytes.


