crossing over
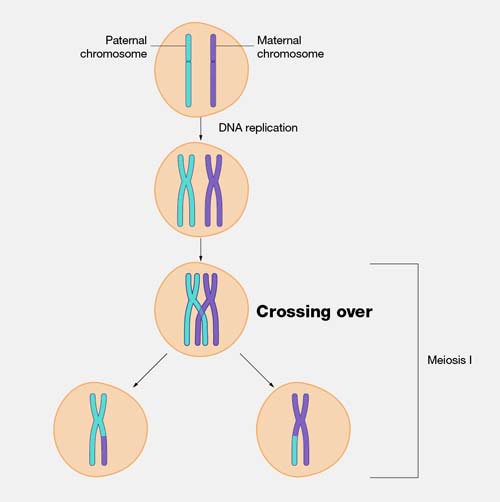
Crossing over is a cellular process that happens during meiosis when chromosomes of the same type are lined up. When two chromosomes — one from the mother and one from the father — line up, parts of the chromosome can be switched.
During cell division, crossing over is a mechanism by which pairs of homologous chromosomes exchange strands of each chromosome, called chromatids. At the end of the first prophase in meiosis, the diverging chromosomes remain in contact at a number of places, called chiasma. Chromatids split and rejoin at each chiasma, with the result that sections of chromatids are exchanged. This alters the distribution of genes also the chromosomes and so gives rise to genetic variation in the resulting gametes, essential in the process of evolution.


