afterburner
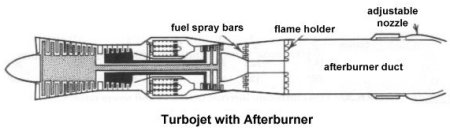
An afterburner is a long tube located between the turbine and the nozzle of a jet engine into which additional fuel can be injected and burned to provide a significant boost in thrust for short periods. Afterburning (or reheat) is a method of augmenting the basic thrust of an engine to improve the aircraft takeoff, climb, and (for military aircraft) combat performance. In an afterburner, fuel is introduced between the engine turbine and the jet pipe propelling nozzle, utilizing the unburned oxygen in the exhaust gas to support combustion. The increase in the temperature of the exhaust gas increases the velocity of the jet leaving the propelling nozzle and therefore increases the engine thrust. This increased thrust could be obtained through use of a larger engine but at the cost of a significant additional weight to the aircraft.
Afterburners can be fitted to both turbojet and turbofan engines. The disadvantage of them is that they greatly increase fuel consumption during the periods they are working.


