annihilation
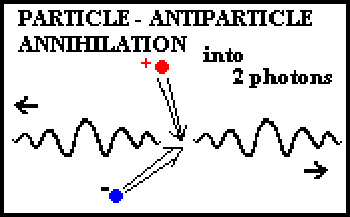
Annihilation is the process in which the entire mass of two colliding particles, one of matter and one of antimatter, is converted into radiant energy in the form of gamma rays or mesons. In the case of a collision between an electron and a positron (anti-electron), which have a combined rest mass of 1.02 MeV, the result is two gamma rays each with a characteristic energy of 0.511 MeV. When nucleons annihilate each other the result is mesons.


