tonsils
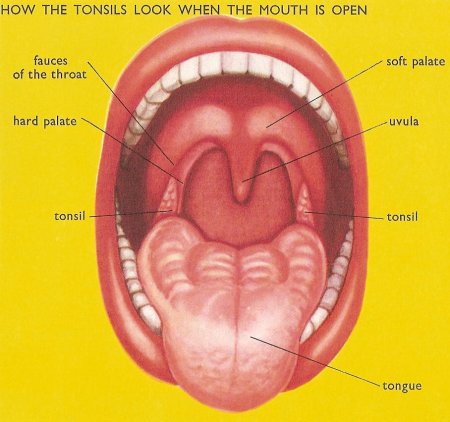
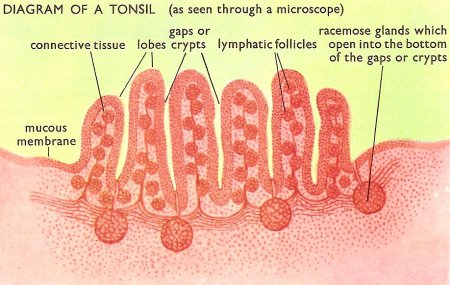
The tonsils ae clusters of lymphatic tissue just under the mucous membranes that line the nose, mouth, and pharynx (throat). There are three groups of tonsils.
The pharyngeal tonsils are located near the opening of the nasal cavity into the pharynx. When these tonsils become enlarged they may interfere with breathing and are called adenoids.
The palatine tonsils are the ones that are located near the opening of the oral cavity into the pharynx.
The lingual tonsils are located on the posterior surface of the tongue, which also places them near the opening of the oral cavity into the pharynx.
Lymphocytes and macrophages in the tonsils provide protection against harmful substances and pathogens that may enter the body through the nose or mouth.
Tonsillitus
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils due to virus or bacterial infection. It may follow sore throat or other pharyngeal disease or it may be a primary tonsil disease. Sore throat and red swollen tonsils, which may exude pus or cause swallowing difficulty, are common; lymph nodes at the angle of the jaw are usually tender and swollen.
Quinsy
Quinsy is an acute complication of tonsillitis in which abscess formation causes spasm of the adjacent jaw muscles, fever, and severe pain. Incision and drainage of the pus produce rapid relief. Antibiotic treatment for the bacterial cause usually leads to a resolution but removal of the tonsils is needed in a few cases.


