tyrosine
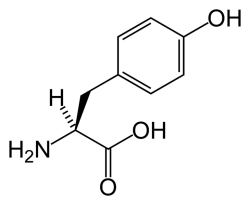
Tyrosine.
Tyrosine is one of the 20 amino acids used by living cells to synthesize proteins. Tyrosine, (OHC6H4CH2CH(NH2)COOH), is not normally an essential amino acid in humans since it can be synthesized from phenylalanine. However, when the enzyme that catalyzes the transformation of phenylalanine to tyrosine is not active because of a hereditary defect, the serious disease known as phenylketonuria (PKU) results.
Tyrosine is found in small amounts in most proteins. The hormone insulin and the enzyme papain (found in papaya fruit) are particularly rich in it, containing about 13 percent by weight. Tyrosine was first isolated, from casein, in 1849.
Tyrosine is the biochemical precursor of many important catecholamines, including adrenaline (epinephrine), noradrenaline (norepinephrine), and dopamine, the thyroid hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine, and the pigment melanin found in skin and hair.


