Ursa Minor
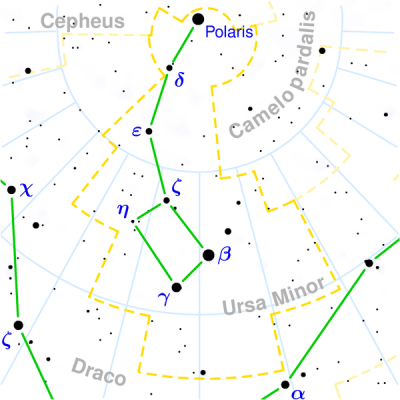
Figure 1. Ursa Minor. © 2003 Torsten Bronger.

Figure 2. The stars of the Little Dipper.

Figure 3. Polarissima_Borealis.
Ursa Minor (abbreviation: UMi), the Little Bear, is a constellation near the north celestial pole that is almost completely surrounded by Draco. Its seven brightest stars form the asterism known as the Lttle Dipper. The stars Beta Ursae Minoris (Kochab) and Gamma UMi (Pherkad) are often called the Guardians of the Pole.
In Greek mythology, Zeus had a son (Arcas) with Callisto, a mortal. In a fit of rage, his wife Hera turned Callisto into a bear, immortalised in the stars as Ursa Major. When Arcas nearly killed his mother as he didn't know who she was, Zeus turned Arcas into a smaller bear – Ursa Minor.
Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, because of Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris) being the North Star.
Little Dipper
The Little Dipper is an asterism formed by the seven brightest stars of Ursa Minor, the most conspicuous of which are the North Star and the two front bowl stars, Kochab (Beta) and Pherkad (Gamma). The handle of the Dipper is the Little Bear's tail and the Dipper's bowl is the Bear's flank. The Little Dipper looks like a miniature and much fainter version of the well-known Big Dipper.
See below for details of the constellation's brightest stars.
| Stars brighter than magnitude 4.0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| star | vis mag | abs mag | spec type | distance (ly) | RA (h m s) | Dec (° ' ") |
| Alpha (Polaris) | 1.97v | -3.64 | F7Ibv | 431 | 02 31 50 | +89 15 51 |
| Beta (Kochab) | 2.07 | -0.88 | K4IIIBa0.3 | 126 | 14 50 42 | +74 09 19 |
| Gamma (Pherkad) | 3.00 | -2.84 | A3II | 480 | 15 20 44 | +71 50 02 |
Polarissima Borealis
Polarissima Borealis (NGC 3172) is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Minor, which is the closest NGC object to the North Celestial Pole (Figure 3). Because of its proximity – less than 1 degree from that most northerly declination – it received the name Polarissima Borealis. Seeing NGC 3172 is a challenge for an observer with a 12-inch telescope.
| visual magnitude | 13.6 |
| angular size | 1.0' × 0.7' |
| position | R.A. 11h 50m, Dec. +89° 7' |
Ursa Minor Dwarf
 |
| Image credit: Mischa
Schirmer.
|
The Ursa Minor Dwarf is a dwarf spheroidal or elliptical system, consisting mostly of old stars, that is one of the small satellite galaxies of the Milky Way. It was discovered by A. G. Wilson at Lowell Observatory in 1954.
| apparent size | 41' × 26' |
| distance | 240,000 light-years |
| position | R.A. 15h 8.8m, Dec. +67° 12' |
| Constellations |
| Andromeda | Antlia | Apus | Aquarius | Aquila | Ara | Aries | Auriga | Bootes | Caelum | Camelopardalis | Cancer | Canes Venatici | Canis Major | Canis Minor | Capricornus | Carina | Cassiopeia | Centaurus | Cepheus | Cetus | Chamaeleon | Circinus | Columba | Coma Berenices | Corona Austrina | Corona Borealis | Corvus | Crater | Crux | Cygnus | Delphinus | Dorado | Draco | Equuleus | Eridanus | Fornax | Gemini | Grus | Hercules | Horologium | Hydra | Hydrus | Indus | Lacerta | Leo | Leo Minor | Lepus | Libra | Lupus | Lynx | Lyra | Mensa | Microscopium | Monoceros | Musca | Norma | Octans | Ophiuchus | Orion | Pavo | Pegasus | Perseus | Phoenix | Pictor | Pisces | Piscis Austrinus | Puppis | Pyxis | Reticulum | Sagitta | Sagittarius | Scorpius | Sculptor | Scutum | Serpens | Sextans | Taurus | Telescopium | Triangulum | Triangulum Australe | Tucana | Ursa Major | Ursa Minor | Vela | Virgo | Volans | Vulpecula |


