units of force, energy, and power
dyne
A dyne is the unit of force in the CGS units system. It is defined as the force needed to impart an acceleration of 1 centimeter per second per second (1 cm s–2) to a mass of one gram. One dyne is equal to 0.00001 newton in the SI system.
electron volt
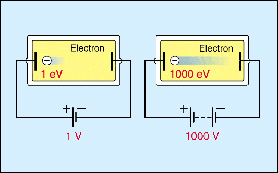 |
An electron volt (eV), also written electronvolt or electron-volt, is a unit of energy equal to the amount of kinetic
energy an electron gains after being accelerated
through an electric potential of 1 volt in
a vacuum. The electron volt is about 1.60219 × 10–19 joules.
The electron volt can also be used as a unit of mass by applying Einstein's relation E = mc 2. For
example, the mass of the proton is 938.256 × 106 eV (938.256
MeV).
Chemically, for 1 mole of electrons 1 eV ~
100 kJ mol–1 (96.49 kJ mol–1).
One electron volt is roughly half the energy carried by a single photon
of red light. The minimum amount of energy needed to ionize hydrogen from
its ground state is 13.6 eV.
The larger units MeV (= 106 eV), GeV (= 109 eV), and
TeV (= 1012 eV) are also used.
erg
The erg is a unit of work or energy in the CGS system, equal to the work done when the point of application of aforce of one dyne is displaced through a distance of one centimeter in the direction of the force. 1 erg = 10–1 joule.
foot-pound
The foot-pound (weight) or foot-pound-force (ft. lbf), a unit of work, is the work done when a mass of one pound is lifted through one foot against gravity, equal to 1.35582 joules.
horsepower
The horsepower (hp) is a unit of power. It is still used commonly
in the United States and, more generally, to measure the power of engines.
Horsepower is defined as the amount of power that can move a 550-pound object
1 foot in one second of time, or 550 feet. × (lb/s). Another way of thinking
about this is that a 1 horsepower (hp) engine can move a 550-pound car 1
foot within one second. So, a 10-horsepower engine can move a 550-pound
car 10 feet within one second. The name comes from the original definition
of the unit by James Watt in the eighteenth century: the weight, 550 pounds, a horse
could raise 1 foot in one second.
Shaft horsepower,
also called brake horsepower, is a measure of the actual
mechanical energy per unit time delivered to a turning shaft. In large reciprocating
engines, indicating horsepower is determined from the pressure
in the cylinders. Boiler horsepower is a measure of the
maximum rate to heat output of a steam generator (1 boiler hp = 33,479 Btu).
Although horsepower is generally used to rate automobile and airplane engines,
and is also commonly used in the United States, the watt (or kilowatt –1000 watts), its metric equivalent, is the standard
international unit of power. 1 hp = 745.7 watts.
joule
The joule (J) is a derived unit of energy in the SI system of units. It is named after the English physicist James Joule. 1 joule is the energy used (or the work done) by a force of one newton in moving its point of application one meter in the direction of the force; also equivalent to the energy dissipated by 1 watt in one second, it equals 107 erg in CGS units. In older units, 1 Btu = 1,055 joules; 1 joule per second = 0.737 ft-lb/s.
One joule is also the work done when a one ampere current is passed through a resistance of one ohm for one second.
newton
The newton (N) is the derived unit of force in the SI system of units. One newton (N) is defined as the force required to give a mass of 1 kilogram an acceleration of 1 m s–2. One kilogram weighs 9.807 N; one pound weight equals 4.45 N. The unit is named after Isaac Newton.
watt
The watt (W) is the derived unit of power in the SI system of units. 1 watt is defined as the consumption of energy at the rate of 1 joule per second. It is named after the Scottish engineer James Watt.
One ampere of current flowing at a potential of one volt produces one watt of electric power. One watt equals 1/746 horsepower. One megawatt = 1 million watts, and is a standard measure of electric power plant generating capacity. One gigawatt (GW) = 1 billion watts.


