halogen
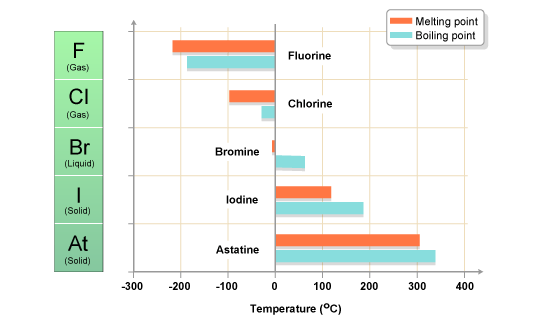
The halogens have low melting points and boiling points, a property typical of non-metals. Fluorine has the lowest melting point and boiling point. The melting points and boiling points then increase down the group..
A halogen is any of a group of chemically related, highly reactive, nonmetallic elements (see nonmetal) that fall in group VIIA of the periodic table. The halogens are:
· fluorine
· chlorine
· bromine
· iodine
· astatine
The general symbol X is often used; the elements have molecular formula X2 (i.e., they are diatomic).
The halogens show a regular gradation of physical and chemical properties: with increasing atomic number, they become less volatile, darker in color, less reactive (in particular, less strongly oxidizing), and less electronegative (see electronegativity).
The typical compounds of the halogens are the halides (containing negative ions of the type F- (fluoride) and Cl– (chloride)), with oxidation number –1; compounds with positive oxidation numbers (usually 1, 3, 5, and 7) are also formed, with increasing stability down the group. The halogens react vigorously with almost all other elements and with organic compounds because they require only one electron to achieve a stable noble gas configuration; for this reason they always occur combined in nature. The name "halogen" means "salt-producer."
Interhalogen
An interhalogen is a binary compound of one halogen with another. Interhalogens have the general formula XX'n, where X' is the more electronegative halogen, and n = 1, 3, 5, or 7. They are volatile, covalent, reactive substances. Bromine (III) fluoride (BrF2) is a very powerful fluoridating agent, and a good solvent for fluorine compounds. Polyhalide salts, containing ions XX'n+1–, are formed by reacting halogens or interhalogens with halide.
Pseudohalogen
Pseudohalogens are a class of monovalent inorganic radicals which chemically resemble the halides and halogens. They include cyanide (CN–) and cyanogen ([CN]2), cyanate (OCN–), thiocyanate (SCN–), and azide (N3–).
Halogenation
Halogenation is the introduction of one of the halogen elements – fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, or astatine – into an organic compound either by addition or substitution of an atom or group of atoms. This reaction is widely used in making pharmaceuticals and dyes.


