lumbar vertebra
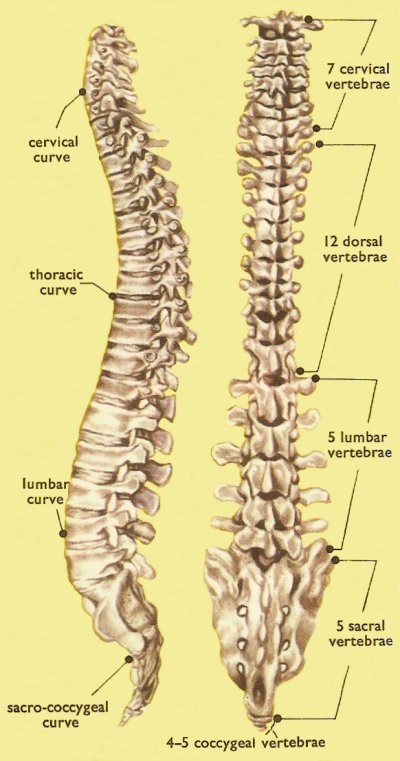
Spinal column, lateral and posterior views.
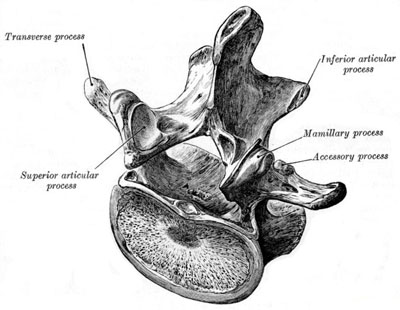
Lumbar vertebra, posterosuperior aspect. Gray's (1918).
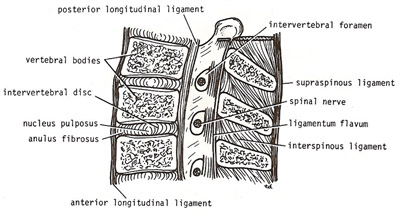
Sagittal section of the lumbar part of the spinal column, showing intervertebral disks and ligaments. From Clinical Anatomy for Medical Students (3rd ed.) by Richard S. Snell.
A lumbar vertebra is any of the 5 vertebra in the spinal column that are situated between the lowest (12th) thoracic vertebra and the sacrum, in the lower part of the back. They are labeled L1 to L5. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest of the unfused vertebrae and have stout processes for attachment of the strong muscles of the lower back.
Detailed anatomy
The body of each lumbar vertebra is massive and kidney-shaped (see second diagram down), and has to bear the greater part of the body weight. The pedicles are strong and directed backward. The laminae are thick and enclose a small triangular vertebral foramen. The transverse processes are long, with sharp ends. The spinous process is short and flat and projects straight back. The superior articular processes face medially, and the inferior articular processes face laterally.
The lumbar vertebrae have no facets for articulation with the ribs and no foramina in the transverse processes. The fifth lumbar vertebra articulates with the base of the sacrum at the lumbosacral joint.
The intervertebral disks in the lumbar region are thicker than in other regions of the spinal column (see bottom diagram). They are wedge-shaped and are responsible for he normal lordosis (curvature of the spine) found in the lumbar region.
Movements of the spine in the lumbar region
In the lumbar region of the spine, flexion is produced by the rectus abdominis and the psoas muscles. Extension is produced by the post vertebral muscles. Lateral flexion is produced by the postvertebral muscles, the quadratus lumborum, and the oblique muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall. The psoas may also play a part in this movement. Rotation is produced by the rotatores muscles and the oblique muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall.
Medical conditions and procedures associated with lumbar vertebrae
Lower back pain (lumbago) is a common condition that may be due to a variety of disorders of varying severity, often associated with the lumbar region of the spine. A lumbar puncture is a procedure to remove a sample of cerebrospinal fluid or to inject drugs or other substances, typically between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae.


